Language 🇺🇸 English (US)
Overview
Implementation
Behind the Scenes
With FastComments, you can invoke an API endpoint whenever a comment is added, updated, or removed from our system.
We accomplish this with asynchronous webhooks over HTTP/HTTPS.
What Are Webhooks 
A Webhook is a mechanism, or an integration, between two systems where the "producer" (FastComments) fires an event that the "consumer" (you) consumes via an API call.
Supported Events & Resources 
FastComments supports webhooks for the Comment resource only.
We support webhooks for comment creation, removal, and updates.
Each of these is considered a separate event in our system and, as such, has different semantics and structures for the webhook events.
Local Development Setup 
For Local development, use a tool like ngrok.
In order to simplify keeping the system secure, local development follows the same process as setting up and securing other environments.
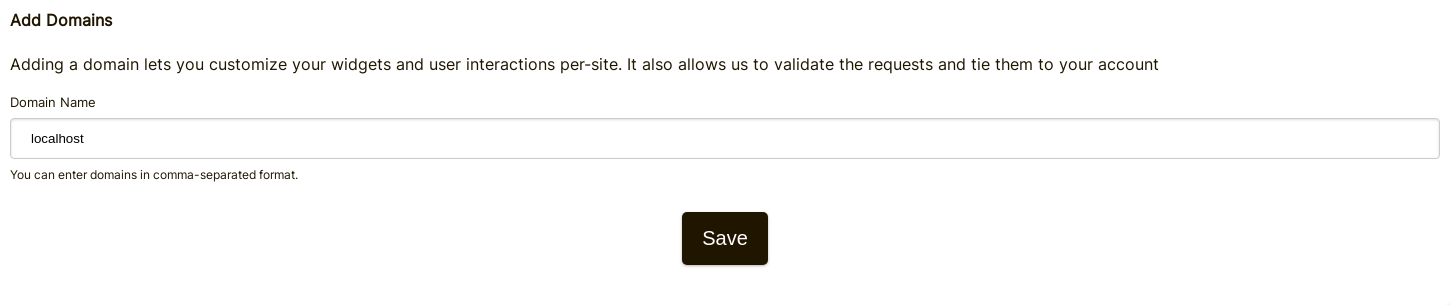
Step 1: Add "localhost" to domains in your account.
Add "localhost" as a domain here.
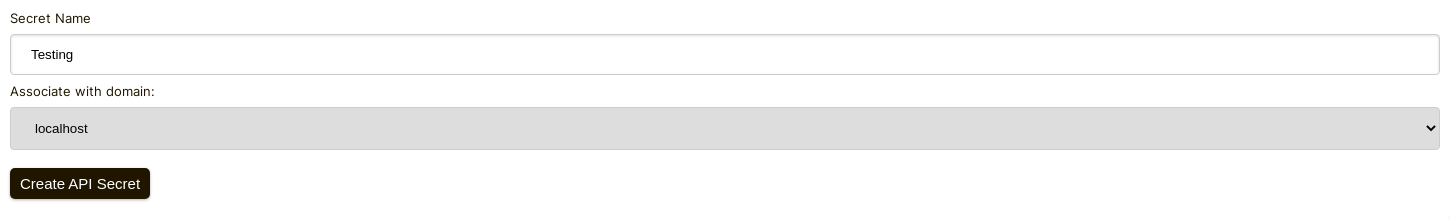
Step 2: Pick an API Key
We're going to be adding webhook configuration for your domain, so we'll need an API key. You can do that here.
Under "Associate with domain" - select your "localhost" domain.
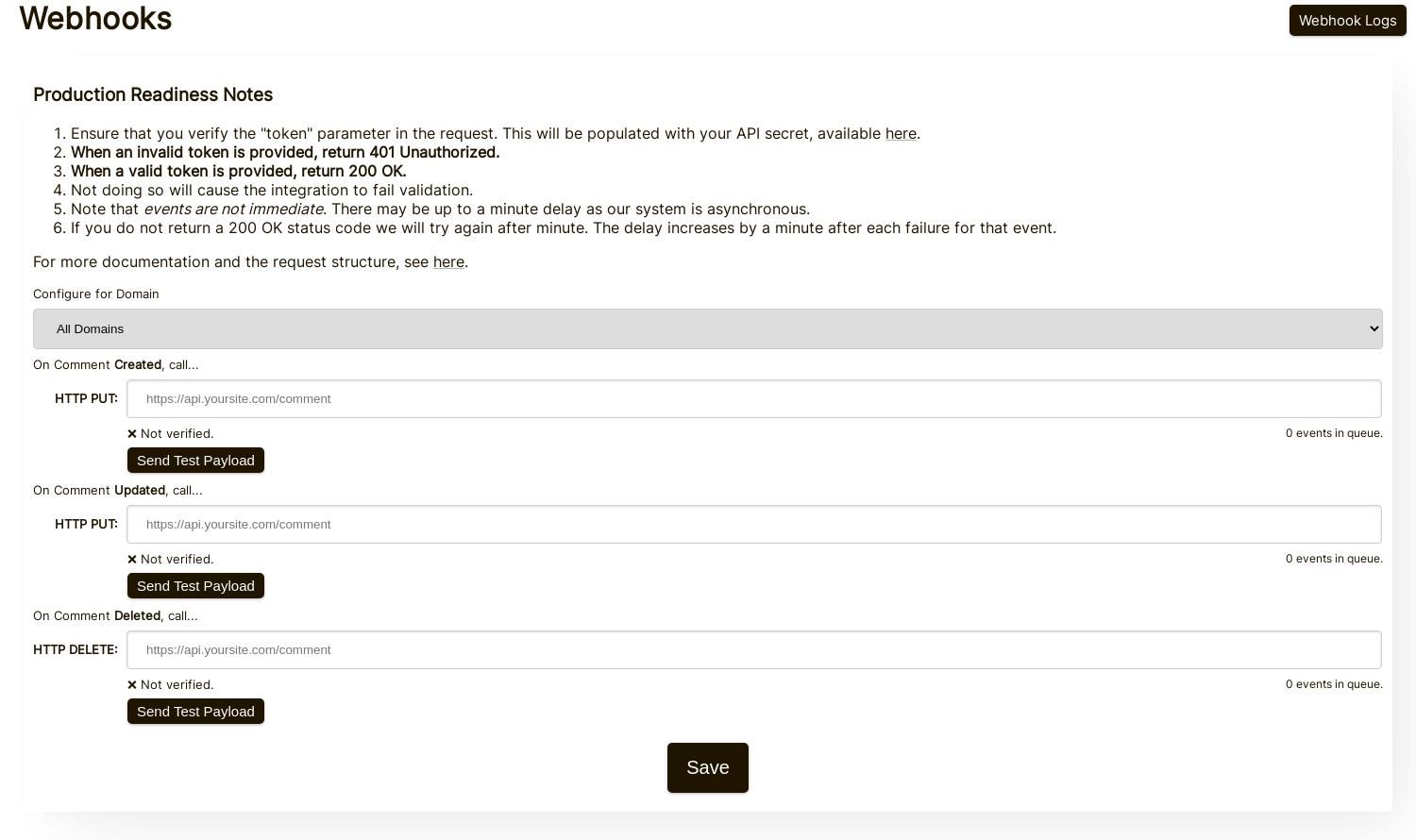
NOTE: Alternatively, you can use one API Secret for all testing activity and staging environments. Simply add an API Secret for "All Domains", and give it a name like "test".
Ensure you have an API Secret defined for your production domain(s). Events for all other domains will use the wildcard (testing) secret.
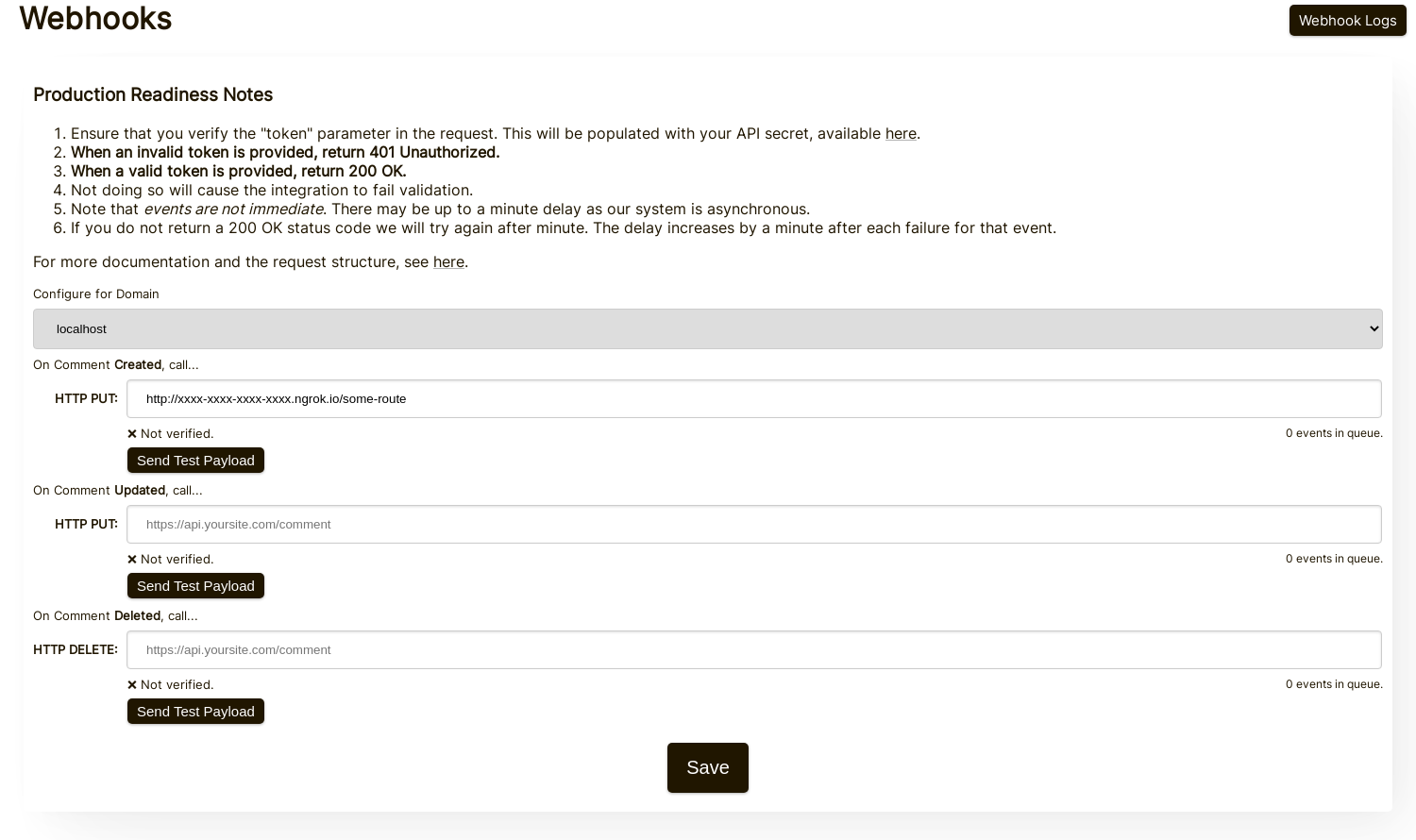
Step 3: Add Your Webhook
While running ngrok or similar tool, set the value for "localhost" here.
When clicking Send Test Payload, we will send two test events to check that you validate the API key.
Once it validates, hit Save.
Step 4: Add A Comment
Now you can add, edit, or delete comments and should see us call your local development machine with the events, using your testing API key. There may be up to 30 seconds delay for the events to reach your machine.
Setup 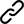
Follow the same steps for localhost as you would for production. Ensure you have production domains and API Secrets set up.
First, navigate to the Webhooks admin. This is accessible via Manage Data -> Webhooks.
The configuration page appears as follows:
On this page you can specify endpoints for each type of comment event.
For each type of event, be sure to click Send Test Payload to ensure you've set up your integration correctly. See the next section, "Testing", for details.
Testing 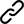
In the Webhooks admin there are Send Test Payload buttons for each event type (Create, Update, Delete). The Create and Update events send a dummy WebhookComment object, while testing Delete will send a dummy request body with just an ID.
Verifying Payloads
When testing your webhook integration, verify the incoming requests include the following headers:
token- Your API SecretX-FastComments-Timestamp- Unix timestamp (seconds)X-FastComments-Signature- HMAC-SHA256 signature
Use the HMAC signature verification to ensure payloads are authentic.
Testing Tools
You can use tools like webhook.site or ngrok to inspect incoming webhook payloads during development.
Event Types
- Create Event: Triggered when a new comment is created. Default method: PUT
- Update Event: Triggered when a comment is edited. Default method: PUT
- Delete Event: Triggered when a comment is deleted. Default method: DELETE
Each event includes the full comment data in the request body (see Data Structures for the payload format).
Data Structures 
The only structure sent via webhooks is the WebhookComment object, outlined in TypeScript below.
The WebhookComment Object Structure
The "Create" Event Structure
The "create" event request body is a WebhookComment object.
The "Update" Event Structure
The "update" event request body is a WebhookComment object.
The "Delete" Event Structure
The "delete" event request body is a WebhookComment object.
Change as of Nov 14th 2023
Previously the "delete" event request body only contained the comment id. It now contains the full comment at the time of deletion. Run
Run 
When users are tagged in a comment, the information is stored in a list called mentions. Each object in that list
has the following structure.
 Run
Run 
HTTP Methods
You can configure the HTTP method for each webhook event type in the admin panel:
- Create Event: POST or PUT (default: PUT)
- Update Event: POST or PUT (default: PUT)
- Delete Event: DELETE, POST, or PUT (default: DELETE)
Since all requests contain an ID, Create and Update operations are idempotent by default (PUT). Repeating the same Create or Update request should not create duplicate objects on your side.
Request Headers
Each webhook request includes the following headers:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
Content-Type |
application/json |
token |
Your API Secret |
X-FastComments-Timestamp |
Unix timestamp (seconds) when the request was signed |
X-FastComments-Signature |
HMAC-SHA256 signature (sha256=<hex>) |
See Security & API Tokens for information on verifying the HMAC signature.
Security & API Tokens 
FastComments webhook requests include multiple authentication mechanisms for security.
Headers Sent
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
token |
Your API Secret (for backwards compatibility) |
X-FastComments-Timestamp |
Unix timestamp (seconds) when the request was signed |
X-FastComments-Signature |
HMAC-SHA256 signature of the payload |
HMAC Signature Verification (Recommended)
We strongly recommend verifying the HMAC signature to ensure webhook payloads are authentic and haven't been tampered with.
Signature Format: sha256=<hex-encoded-signature>
How the signature is computed:
- Concatenate:
timestamp + "." + JSON_payload_body - Compute HMAC-SHA256 using your API Secret as the key
- Hex-encode the result
Example Verification (Node.js)
const crypto = require('crypto');
function verifyWebhookSignature(req, apiSecret) {
const timestamp = req.headers['x-fastcomments-timestamp'];
const signature = req.headers['x-fastcomments-signature'];
if (!timestamp || !signature) {
return false;
}
// Verify timestamp is recent (within 5 minutes)
const now = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
if (Math.abs(now - parseInt(timestamp, 10)) > 300) {
return false; // Replay attack prevention
}
// Verify signature
const payload = JSON.stringify(req.body);
const expectedSignature = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', apiSecret)
.update(`${timestamp}.${payload}`)
.digest('hex');
return signature === `sha256=${expectedSignature}`;
}Example Verification (Python)
import hmac
import hashlib
import time
import json
def verify_webhook_signature(headers, body, api_secret):
timestamp = headers.get('X-FastComments-Timestamp')
signature = headers.get('X-FastComments-Signature')
if not timestamp or not signature:
return False
# Verify timestamp is recent
now = int(time.time())
if abs(now - int(timestamp)) > 300:
return False
# Verify signature
payload = json.dumps(body, separators=(',', ':'))
message = f"{timestamp}.{payload}"
expected = hmac.new(
api_secret.encode(),
message.encode(),
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
return signature == f"sha256={expected}"Example Verification (PHP)
function verifyWebhookSignature($headers, $body, $apiSecret) {
$timestamp = $headers['X-FastComments-Timestamp'] ?? null;
$signature = $headers['X-FastComments-Signature'] ?? null;
if (!$timestamp || !$signature) {
return false;
}
// Verify timestamp is recent (within 5 minutes)
$now = time();
if (abs($now - intval($timestamp)) > 300) {
return false;
}
// Verify signature
$payload = json_encode($body, JSON_UNESCAPED_SLASHES);
$message = $timestamp . '.' . $payload;
$expectedSignature = 'sha256=' . hash_hmac('sha256', $message, $apiSecret);
return hash_equals($expectedSignature, $signature);
}Legacy Authentication
The token header containing your API Secret is still sent for backwards compatibility. However, we recommend migrating to HMAC verification for improved security as it protects against replay attacks.
How It Works & Handling Retries 
All changes to the Comment object in the system trigger an event that ends up on a queue.
The initial webhook event is usually sent within six seconds of the event source occurring.
You can monitor this queue in the Webhooks admin in the event that your API goes down.
If a request to your API fails, we'll requeue it on a schedule.
That schedule is 1 Minute * the retry count. If the call fails once, it'll try again in
a minute. If it fails twice, it'll then wait two minutes, and so on. This is so that we
don't overload your API if you're going down for load-related reasons.
Webhooks can be canceled from the logs page.
In Conclusion
This concludes our Webhooks documentation.
We hope you find the FastComments Webhook integration easy to understand and fast to set up.
If you feel you have identified any gaps in our documentation, let us know below.